Spins and Turns
Understanding Axes
Of the many reasons why people fall off balance during turns, by far the most prevalent is the tendency to pull away from the axis of rotation. This normally happens when the dancer does not have an understanding (or at least an innate awareness) of the axis that the body should be rotating around. It will therefore help you considerably to gain an understanding of axes, and ultimately to develop an awareness and a sensitivity to the axis of specific turns.
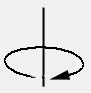
Let's imagine for a second that we're looking at an object from the top view as it rotates. Think of a circle as representing the path that the object rotates around, while the center point of the circle represents the axis. See illustration:
The Three Types of Axis
There are 3 categories of axis around which your body will rotate during any kind of turn:
(1) The Center Axis
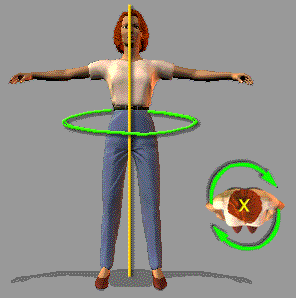
USAGE: Spot rotation with body weight held between feet.
EXAMPLES: Twist Turn.
The center axis runs straight through the middle of the body, from the top of the head, down the spine and straight down from the pelvis to the floor between the feet.
When you turn around your center axis, one side of the body moves forward while the other side moves backward. With both sides of the body moving in opposite directions, the weight remains split between the feet.
It should be noted that the center axis is the least commonly used of all. Rotation around the center axis requires that the weight be split betweem the feet. Most turns that use spot rotation are taken with the weight held over one foot. The center axis is therefore fairly rare, being used only for specialized types of turn such as the Twist Turn.
(2) The Left and Right Side Axes
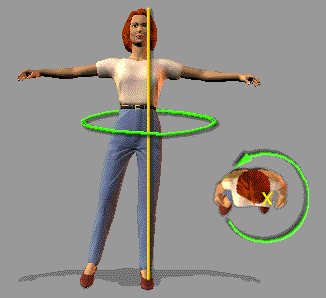
USAGE: Spot rotation with body weight held over one foot.
EXAMPLES: Pencil Turn, Spot Turn, Outside Swivels, Ochos.
The left-side axis runs through the body from the left shoulder through the left hip and left foot. The right-side axis runs through the body from the right shoulder through the right hip and right foot. (Left-side axis is shown).
When you turn with the weight held over one foot, you will use the axis according to which foot you are standing on: Turning on the left foot uses the left-side axis, while turning on the right foot uses the right-side axis. Since most non-progressive turns occur with the weight over one foot, these are the axes which you will be using most often.
The most common mistake when attempting to turn over one foot is to use the center axis instead of the side axis. This will inevitably cause you to fall off balance, forcing you to take an extra step. Exercises at the end of this lesson will focus on correcting this error.
(3) The Outside Axes

USAGE: Progressive rotation.
EXAMPLES: Pivots, Chain Turns, Three-Step Turn, Waltz Box Step, Viennese Left Cross Turn.
The outside axis is completely outside the body. Instead of rotating around itself, the body revolves around a fixed point in space, much like the Earth revolves around the sun.
When the axis is outside the body, the body must rotate progressively. The turn therefore occurs between two steps, or over the course of more than two steps. It is not possible to take progressive rotation while staying on one foot.





